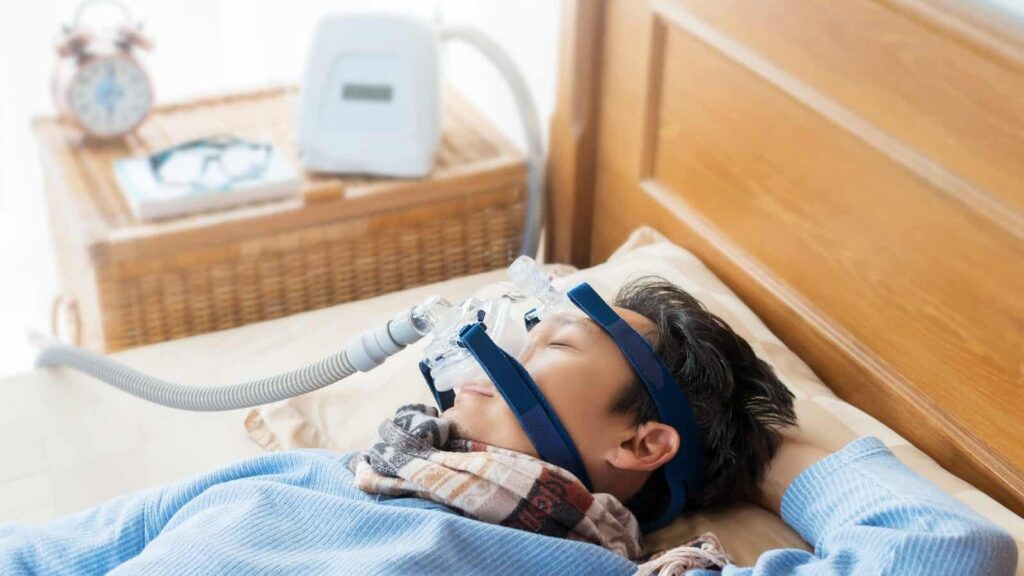
Sleep Apnea is found in young and older adults worldwide. Based on statistics, many people are struggling with the sleep epidemic. An expert sleep specialist established that about 60% of people worldwide could not sleep for up to 6-8 hours comfortably. Moreover, about 37% sleep during the day, which suggests they don’t sleep well at night due to the effects of sleep disorders.
Of course, people have a lot of reasons to stay awake at night. But, many people suffer from a medical condition that prevents them from getting good sleep at night. Worse, most sleep apnea patients don’t understand the essence of treating sleep apnea when the symptoms are still mild. Hence, they allow things to get out of hand. That’s why everyone needs to learn about sleep apnea.
How do you know if you are among sleep apnea patients?
In this write-up, we will expose you to how to prevent sleep apnea solutions or do a simple self-diagnosis by telling you the types, symptoms, and causes of sleep apnea. You will also learn about some risk factors and complications when refusing to treat sleep apnea on time.
What is Sleep Apnea syndrome?
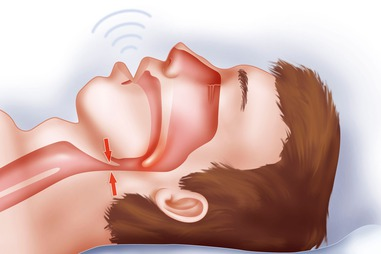
Sleep apnea is a disorder in which people start and stop breathing repeatedly. It may also cause difficulty in falling asleep at any time of the day. For example, you might have moderate sleep apnea if you feel tired after a whole night’s sleep.
For the records, there are three main types of sleep apnea. They include:
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): it is the more prevalent form of sleep apnea that occurs when your throat muscles relax and block the airflow into the lungs
- Central sleep apnea (CSA) happens when the brain does not send proper signals to specific muscles that control breathing, causing an inability to sleep.
- Treatment-emergent central sleep apnea (complex sleep apnea): this sleep disorder happens when someone has obstructive sleep apnea — diagnosed with a sleep study — that converts to central sleep apnea when receiving therapy for obstructive sleep apnea.
If you think you might have central or obstructive sleep apnea, see your healthcare provider. Treatment can ease your symptoms of sleep disorders and might help prevent heart attacks and other complications.
What Are the Symptoms of Sleep Apnea?
The symptoms of central and obstructive sleep apnea overlap, sometimes making it tougher to determine which type is battling your airway. The most common symptoms of central and obstructive sleep apnea include:
- Gasping for air during sleep.
- Awakening with a dry mouth.
- Morning headache.
- Loud snoring.
- Insomnia.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness,
- Difficulty paying attention while awake.
- Irritability.
The Major Causes of Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Anyone can develop sleep apnea for several factors. For example, you can develop obstructive sleep apnea when the throat muscles relax and block the air passage.
Mild obstructive sleep apnea causes your muscles or airway to relax. It can also narrow or close as you breathe in. As a result, you may not get adequate air, which can lower blood oxygen levels. The brain senses that you can’t breathe and briefly wake you to reopen your airway.
People with obstructive sleep apnea might choke, cough, or gasp for air at intervals when sleeping. This pattern can continue about 30 times in an hour, all night. That makes reaching the restful sleep phases more challenging every day and night.
Central Sleep Apnea
This less common type of sleep apnea can occur when the brain fails to signal to the breathing muscles. That means the patient does not need to breathe for a short period. As a result, people with this disorder might wake up with shortness of breath
What are the Risk Factors of Sleep Apnea
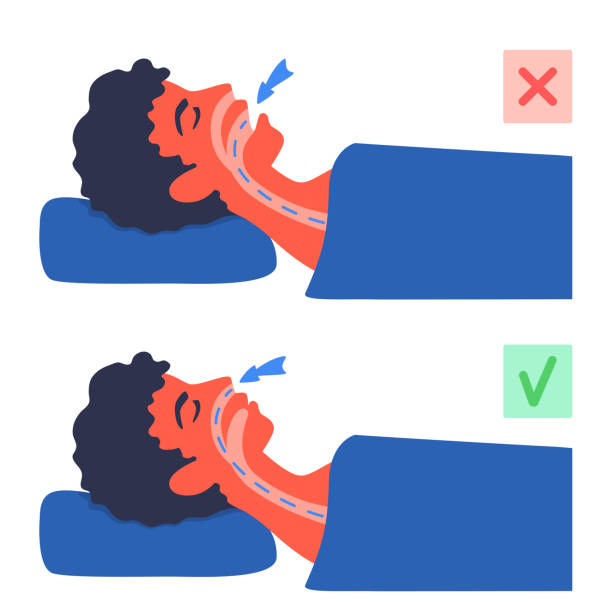
Undiagnosed sleep apnea can affect anyone’s health, including children. But certain factors may increase the risk of developing the symptoms.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
The following are the factors that increase the risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea:
- Excess weight: Obesity increases the risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Fat deposits around the upper air passage can obstruct breathing when sleeping.
- Neck circumference: People with thick necks might struggle with the problems of narrower airways.
- A narrowed airway: You might have inherited a narrow throat. Tonsils or adenoids also can enlarge and block the airway, particularly in children.
- Being male: Men are 2 to 3 times more likely to have moderate obstructive sleep apnea than women. However, women increase the risk if they are going through menopause or are overweight.
- Use of alcohol, sedatives, or tranquilizers
- Family history: Having family members with severe obstructive sleep apnea might increase your risk.
- Smoking: Smokers are more likely to have severe obstructive sleep apnea
- Being older: Sleep apnea occurs more often in older adults.
- Medical conditions: Congestive heart failure, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure are among the conditions that can increase the risk of severe obstructive sleep apnea.
Central Sleep Apnea
The risk factors for this type of sleep apnea include:
- Being a male: Central sleep apnea is more common in men than women.
- Being older: Both middle-aged and older people have a high risk of central sleep apnea.
- Heart disorders: Congestive heart failure increases the risk.
- Stroke: Being a stroke patient can increase the risk of central sleep apnea.
What are the Complications that come with Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a severe medical condition. Complications of Obstructive Sleep Apnea can include:
- High blood pressure or heart problems: Sudden oxygen levels drop during OSA increases blood pressure and strains the cardiovascular system. As a result, having Obstructive Sleep Apnea increases your risk of high blood pressure.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea might also increase the risk of stroke, recurrent heart attack, and irregular heartbeats, such as atrial fibrillation. In addition, if you are nursing heart disease, multiple episodes of low blood oxygen (hypoxia or hypoxemia) can lead to sudden death from an irregular heartbeat.
- Daytime sleepiness/fatigue. As you are waking up at intervals is associated with sleep apnea, making restorative sleep impossible, and causing daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and irritability.
You might have trouble concentrating and falling asleep at work while watching TV or driving. People with severe sleep apnea have an increased risk of motor vehicles and workplace accidents.
You might also feel hot-tempered, moody, or depressed. In addition, children with sleep apnea might perform poorly in school.
- Type 2 diabetes. Sleep apnea increases the risk of developing insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome. This sleep disorder, which includes increased abnormal cholesterol levels, blood pressure, increased waist circumference, and high blood sugar, is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- Complications with medications and surgery. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is also concerned with specific medication and general anesthesia. In addition, people with sleep apnea are likely to have health complications after surgery because they are prone to breathing problems.
Finally
Loud snoring can indicate a severe sleep apnea problem, but not everyone with mild sleep apnea snores. Talk to your sleep specialist if you have symptoms of severe sleep apnea. Also, ask your sleep specialist about any sleep problem that leaves you tired, sleepy, and irritable.
You may also need to learn how to use other treatment options like the continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine to ease you when sleeping at night. Meanwhile, your doctor will determine the type of continuous positive airway pressure machine best for your sleep apnea problems and restore your normal sleep.